SDG target: End preventable deaths of newborns and children under age five, with all countries aiming to reduce under-five mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births.
Pneumonia is the leading infectious cause of child mortality and second only to neonatal disorders as a cause of overall child mortality. However, just 3 percent of global research and development spending and 6 percent of global foreign aid spending on infectious diseases goes to pneumonia. Globally, fewer than half of children are currently protected by the leading pneumonia vaccine. A less expensive vaccine may become available soon, which would enable more countries to protect more children and drive down the global child mortality burden.
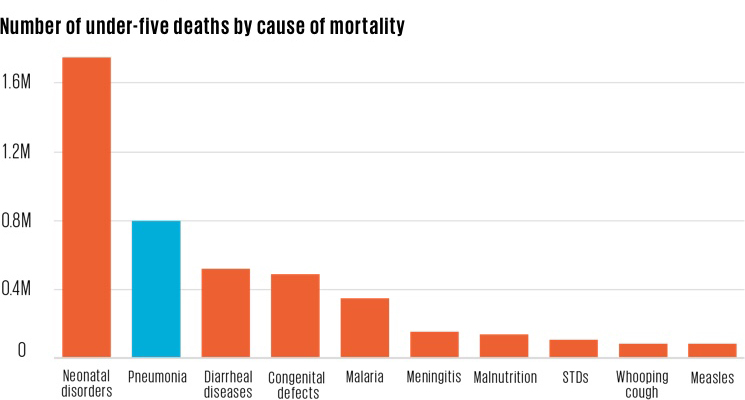
Below is the global progress on this indicator since 1990. Explore progress for specific countries using the drop-down menu below the chart.
Under-five deaths per 1,000 live births
Current projection
If we progress
If we regress